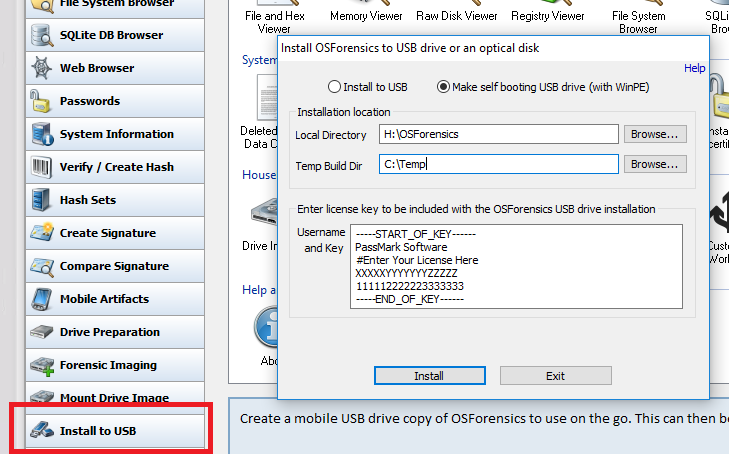
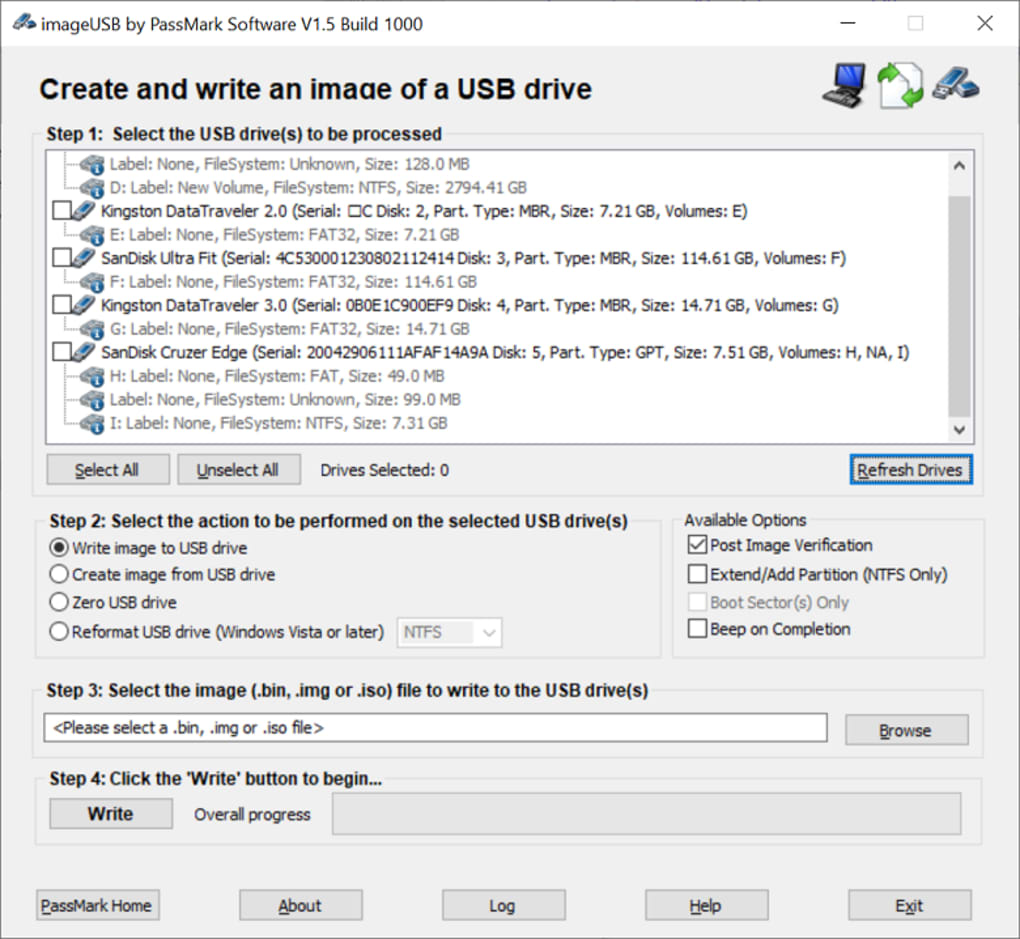
These Controllers need software drivers to operate properly. That’s why your first step is to check that you have the latest USB 2.0 drivers on your system. Start by opening Windows Explorer and right-clicking on My Computer. Click the Hardware tab, followed by the Device Manager Button. Towards the bottom of the list you should see a heading. Device Drivers; Product Finder. ImageUSB can also be used to install OSFClone to a USB Drive for use with PassMark OSForensics. Windows USB/DVD Download Tool. Windows USB 2.0 Application Programming Interface (API) The free USB2 Application Programming Interface has been designed to allow access by third party programs to the PassMark USB 2.0 loop back plug.It provides several functions to communicate with the USB2 loop back plugs as an easy way to use the plugs without having to write any device driver or extra firmware code.
- Passmark Software Usb Devices Driver Download For Windows 7
- Passmark Software Usb Devices Driver Download For Windows 8.1
- Passmark Software Usb Devices Driver Download For Windows 10
- Passmark Software USB Devices Driver Download For Windows
- Passmark Software Usb Devices Driver Download For Windows Xp
USB 2.0 on Windows XP and 2000
There are many reasons why problems with USB devices can occur. Keep in mind that USB Controllers are small pieces of hardware that allow your computer to operate USB connections. These Controllers need software drivers to operate properly. That’s why your first step is to check that you have the latest USB 2.0 drivers on your system.
Start by opening Windows Explorer and right-clicking on My Computer. Click the Hardware tab, followed by the Device Manager Button. Towards the bottom of the list you should see a heading ‘Universal Serial Bus Controllers.’ Click the small plus sign next to it. This menu will expand to reveal one or more listings. To see if you have USB 2.0, look for a line that says ‘USB2 Enhanced Controller.’ The exact entry will vary slightly and don’t confuse it with other entries that may simply list ‘USB Universal Controller’. See the screenshot to the below for an example of how it may look. Note that there are no yellow exclamation points next to the entries – the yellow exclamations, indicate a problem with the device.
If you do see a yellow exclamation next to any of the USB entries, especially the USB2 Enhanced Controller, then there is a problem affecting the USB 2.0 driver on your system. To fix the problem, right click on the entry and select Properties. Click on the 'Troubleshoot' button and follow the prompts. In most cases this will help find a solution. The alternative is to right-click and select 'Update driver' while your computer is connected to the Internet.Passmark Software Usb Devices Driver Download For Windows 7
OK, what if you look down the USB list and there is no entry with 'USB2 Enhanced Controller'? This generally means that you do not have the USB 2.0 driver installed. There are two steps you need to follow. Firstly you must ensure that you have installed either Windows XP Service Pack 3 or Windows 2000 Service Pack 4. Technically, XP users only need Windows XP Service Pack 1, but this would be risky as it leaves your system exposed to numerous security threats fixed with Service Pack 2.If needed, download and install the Service Pack, then restart your system. Go back to the Device Manager - as shown in the first paragraph - and check the status of your USB controllers. If the USB2 Enhanced Controller has appeared without the yellow symbol, you should be ready to use USB 2.0. If not, you will need the specific USB 2.0 driver for your system. There are only six manufacturers of USB 2.0 controllers: Acer Labs, Intel, NEC, SiS, VIA and nVidia (which may appear as 'Standard Controller'), but sometimes they are re-branded by other companies. In this case, you will need to find out which Controller is on your system and visit the manufacturers site for an update or special instructions. For example, if you have the Via USB Controller, you will need the Via USB 2.0 driver (you can download a copy here).
-->
Device Drivers Version Size Download; USB Power Delivery device driver 32 and 64-bit 2.12.28: 2.18 MB: Windows 32-bit and 64-bit Device drivers required for the PassMark USB Power Delivery.
Versions supported
- Windows 10
- Windows 8.1
Applies to
- Device manufacturers of CDC Control devices
Microsoft-provided in-box driver (Usbser.sys) for your Communications and CDC Control device.
Passmark Software Usb Devices Driver Download For Windows 8.1
In Windows 10, the driver has been rewritten by using the Kernel-Mode Driver Framework that improves the overall stability of the driver.
- Improved PnP and power management by the driver (such as, handling surprise removal).
- Added power management features such as USB Selective Suspend.
In addition, UWP applications can now use the APIs provided by the new Windows.Devices.SerialCommunication namespace that allow apps to talk to these devices.
Usbser.sys installation
Load the Microsoft-provided in-box driver (Usbser.sys) for your Communications and CDC Control device.
Note
If you trying to install a USB device class driver included in Windows, you do not need to download the driver. They are installed automatically. If they are not installed automatically, contact the device manufacturer. For the list of USB device class driver included in Windows, see USB device class drivers included in Windows.
Windows 10
In Windows 10, a new INF, Usbser.inf, has been added to %Systemroot%Inf that loads Usbser.sys as the function device object (FDO) in the device stack. If your device belongs to the Communications and CDC Control device class, Usbser.sys is loaded automatically.You do not need to write your own INF to reference the driver. The driver is loaded based on a compatible ID match similar to other USB device class drivers included in Windows.
USBClass_02
USBClass_02&SubClass_02
- If you want to load Usbser.sys automatically, set the class code to 02 and subclass code to 02 in the Device Descriptor. For more information, see USB communications device class. With this approach, you are not required to distribute INF files for your device because the system uses Usbser.inf.
- If your device specifies class code 02 but a subclass code value other than 02, Usbser.sys does not load automatically. Pnp Manager tries to find a driver. If a suitable driver is not found, the device might not have a driver loaded. In this case, you might have to load your own driver or write an INF that references another in-box driver.
- If your device specifies class and subclass codes to 02, and you want to load another driver instead of Usbser.sys, you have to write an INF that specifies the hardware ID of the device and the driver to install. For examples, look through the INF files included with sample drivers and find devices similar to your device. For information about INF sections, see Overview of INF Files.
Note
Microsoft encourages you to use in-box drivers whenever possible. On mobile editions of Windows, such as Windows 10 Mobile, only drivers that are part of the operating system are loaded. Unlike desktop editions, it is not possible to load a driver through an external driver package. With the new in-box INF, Usbser.sys is automatically loaded if a USB-to-serial device is detected on the mobile device.
Windows 8.1 and earlier versions
In Windows 8.1 and earlier versions of the operating system, Usbser.sys is not automatically loaded when a USB-to-serial device is attached to a computer. To load the driver, you need to write an INF that references the modem INF (mdmcpq.inf) by using the Include directive. The directive is required for instantiating the service, copying inbox binaries, and registering a device interface GUID that applications require to find the device and talk to it. That INF specifies 'Usbser' as a lower filter driver in a device stack.
The INF also needs to specify the device setup class as Modem to use mdmcpq.inf. Under the [Version] section of the INF, specify the Modem and the device class GUID. for details, see System-Supplied Device Setup Classes.
For more information, see this KB article.
Configure selective suspend for Usbser.sys
Starting in Windows 10, Usbser.sys supports USB Selective Suspend. It allows the attached USB-to-serial device to enter a low power state when not in use, while the system remains in the S0 state. When communication with the device resumes, the device can leave the Suspend state and resume Working state. The feature is disabled by default and can be enabled and configured by setting the IdleUsbSelectiveSuspendPolicy entry under this registry key:
To configure power management features of Usbser.sys, you can set IdleUsbSelectiveSuspendPolicy to:
'0x00000001': Enters selective suspend when idle, that is, when there are no active data transfers to or from the device.
'0x00000000': Enters selective suspend only when there are no open handles to the device.
That entry can be added in one of two ways:
Write an INF that references the install INF and add the registry entry in the HW.AddReg section.
Describe the registry entry in an extended properties OS feature descriptor. Add a custom property section that sets the bPropertyName field to a Unicode string, 'IdleUsbSelectiveSuspendPolicy' and wPropertyNameLength to 62 bytes. Set the bPropertyData field to '0x00000001' or '0x00000000'. The property values are stored as little-endian 32-bit integers.
For more information, see Microsoft OS Descriptors.
Develop Windows applications for a USB CDC device

Passmark Software Usb Devices Driver Download For Windows 10
If you install Usbser.sys for the USB CDC device, here are the application programming model options:
Passmark Software USB Devices Driver Download For Windows
Starting in Windows 10, a Windows app can send requests to Usbser.sys by using the Windows.Devices.SerialCommunication namespace. It defines Windows Runtime classes that can use to communicate with a USB CDC device through a serial port or some abstraction of a serial port. The classes provide functionality to discover such serial device, read and write data, and control serial-specific properties for flow control, such as setting baud rate, signal states.
In Windows 8.1 and earlier versions, you can write a Windows desktop application that opens a virtual COM port and communicates with the device. For more information, see:
Win32 programming model:
.NET framework programming model: